...
The algorithm works with any cut and has 8 presets. In different presets, the balance of goodness metrics differs, so they can give different results. Users have to select the best result among the 8 presets. For highly asymmetrical models the best result most probably will be achieved with the most aggressive presets (higher values in the DistanceLimit, SymmetryCoeff, and Shift parameters). For the almost ideally symmetrical models, less aggressive presets will be enough. More aggressive presets are able to fix the significant imperfections of the initial model, but they also cause the risk of too much distortion of the model and getting a useless result.
| Note |
|---|
If the SmartNormalize produced 4 results instead of 8, this most likely means that the input model does not have Facet Types. For example, Imported model could not have Facet Types after file opening. To create Facet Types, open the Facet Types menu. Note that after opening you will immediately see the coloring result of "Auto Types" function but not absence of facet types coloring even if model doesn’t have Facet Types. Do not worry, you are doing everything right, before opening the Facet Types menu, the coloring did not exist and program created it as Auto after opening of Facet Types dialog.Check out the current coloring and edit it if required. Close the Facet Types menu, and restart the SmartNormalize. |
Note that weight as a parameter doesn't participate in optimization by the “SmartNormalize” algorithm. So the final solution could be with any weight. It is not important because the purpose of the algorithm is to get the correct model for further work. The results of the “SmartNormalize” work cannot be used as cutting plans.
...
- To improve output, specify facet types for the initial model. This:
- will guarantee deleting of excess facets
is necessary for working with enabled Custom Facet Marking parameter (see above)
Note If the SmartNormalize produced 4 results instead of 8, this most likely means that the input model does not have Facet Types.
For example, Imported model could not have Facet Types after file opening. To create Facet Types, open the Facet Types menu. Note that after opening you will immediately see the coloring result of "Auto Types" function but not absence of facet types coloring even if model doesn’t have Facet Types. Do not worry, you are doing everything right, before opening the Facet Types menu, the coloring did not exist and program created it as Auto after opening of Facet Types dialog.Check out the current coloring and edit it if required. Close the Facet Types menu, and restart the SmartNormalize.
- the facet types are automatically transferred to the resulting model which is useful during registering it as a new in-house cut
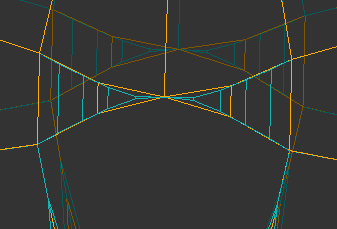
On Stage 1 (see above) the symmetrical sectors of the model which will in Stage 3 become of the same length, may have large differences in length. Because of this, the different number of girdle facets can go to non-symmetrical sectors. This can lead to poor performance of the Smart Recut algorithm for such models. If this situation occurs, it is recommended to run the Smart Normalize algorithm one more time - it should divide a girdle into facets correctly because initially, the sectors have the same length.
Before SN After 1st run of SN After 2nd run of SN a
- The small value of the Shift parameter may block solution search when Custom Facet Marking is enabled.
If all the presets produce distorted models, one of the probable reasons is the errors in the detection of symmetry axes or the pairs of symmetrical facets. This may be caused by the large asymmetry of the initial model or the non-standard number of symmetry axes. In this case try specifying facet types, then set SymmetryCoeff to "0" and run Smart Normalize without Symmetry.
For square cuts, the algorithm enforces the final GidleRatio to 1.0 to reach the corresponding symmetry.
The algorithm can work with the models in which crown and pavilion touch in a vertex or edge. For such cases, the facet types must be specified.
- Nonconvex heart cuts are supported by Smart Normalize and Smart Recut. However, in the case of Hearts, the algorithm more often has difficulties with the girdle shape and finding the correct symmetry axes for the scanned models. Thus for building Heart allocation forms it is better to use the models created in the Cut Designer or the solutions of Recut or Smart Recut algorithms.
...