...
.dmc file name in "Alloc" column for loaded models
Tag "BN" and preset color in "Alloc" column for solutions
Grade by cut Absolute Appraiser
Errors in "Alloc" column tooltip
Color labels (details in next chapter)
SmartNormalize Auto Color
...
Labels
To simplify the choice among SmartNormalize solutions, the algorithm began to place Color labels that warn about the presence of known errors. In SmartNormalize batch mode color labels also determines if the allocation form has been registered automatically.
...
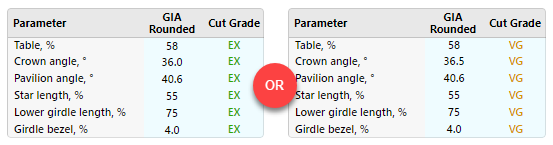
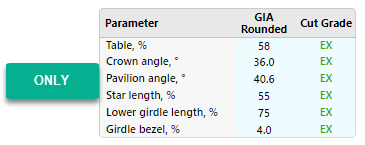
To eliminate this risk, for the Smart Recut algorithm, the new Safe Boundaries mode is added. It is intended to be used when working with Brilliant cut. The mode sets safe distances to a possible GIA rounding. The values are:
| GRID Parameter | Margin | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Table | 0,008 | mm |
| Crown angle | 0,10 | deg |
| Pavilion angle | 0,06 | deg |
| Star length | 1,5 | % |
| Lower girdle length | 1,5 | % |
| Girdle bezel | 0,1 | % |
| Panel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
| Other GIA Cut parameters | Margin | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Girdle valley Min | 0,1 | % |
| Girdle valley Max | 0,1 | % |
| Culet | 0,1 | % |
| Crown painting | 0,2 | deg |
| Pav painting | 0,2 | deg |
| Sum painting | 0,2 | deg |
| Note |
|---|
At the moment, these values cannot be changed - in the future, it is planned to provide a user interface for viewing/editing. |
...
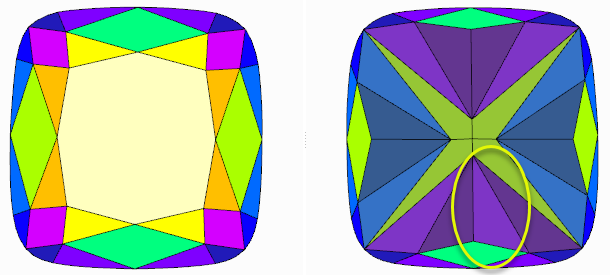
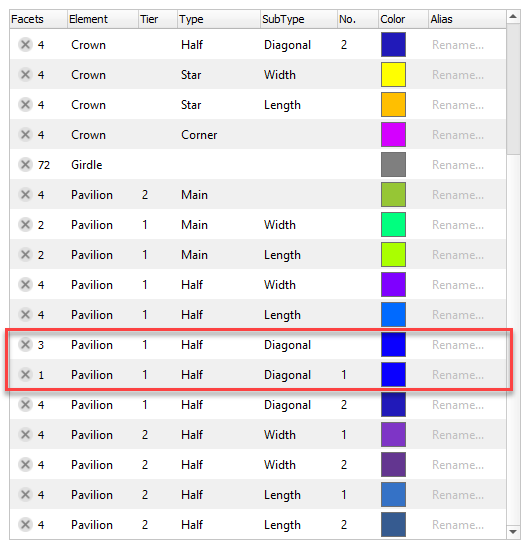
- The algorithm tries to fix facet type mistakes using information about groups of symmetrical facets and which type dominates in a group. If the situation is clear enough, mistakes in facet types are fixed automatically and the algorithm finds the solution with the correct number of symmetry axes. If the case is too complex, the algorithm uses initial facet types without changes.
- Fixing does not change the initial model facet types but does change the resulting model - it will have different (fixed) facet types.
Example:
| Easy to see with the eyes | Not obvious to an operator | |
|---|---|---|
| Initial model | ||
| Normalized model |
Control absolute value azimuths for in-house cuts
...