
| All calculation are performed in 2D. Model is projected on table facet plane |
1.1 Draw a line a through star facet edge belongs to table. Line will separate plane into half-planes β and δ:
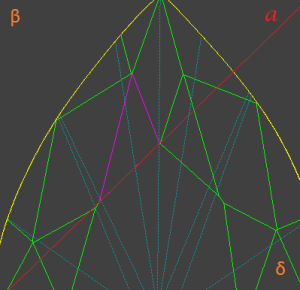
1.2 Find most distant point (call it B) on star facet from line a. A is point, where perpendicular from point B is crossing line a:
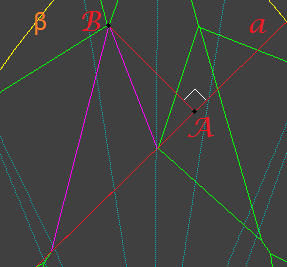
1.3 Find most distant point on girdle (call it D) from line a, point should belong to β half-plane. C is point, where perpendicular from point D is crossing line a:

1.4 Star Upper ratio is |AB| length divided by |CD| length.

| All calculation are performed in 2D. Model is projected on table facet plane |
2.1 Draw a line a through star facet edge belongs to table. Line will separate plane into half-planes β and δ:
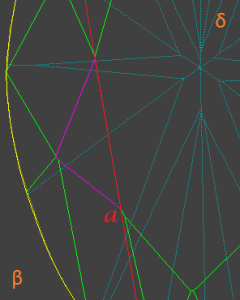
2.2 Find most distant point (call it B) on star facet from line a. A is point, where perpendicular from point B is crossing line a:
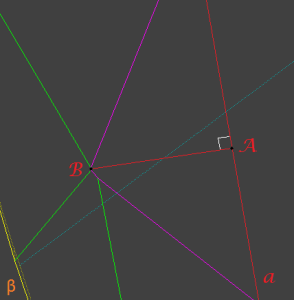
2.3 Find most distant point on girdle (call it D) from line a, point should belong to β half-plane. C is point, where perpendicular from point D is crossing line a:
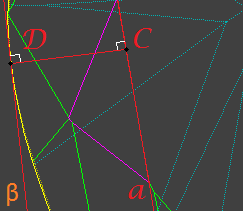
2.4 Star Upper ratio is |AB| length divided by |CD| length.
slkfjlskdfjslf