...
- That you want to register as your in-house cut
- That you want to add as an allocation form to the existing cut
That you want to use as a sample during scanning
See details on each of these scenarios in the sections below.Info title Note You can also apply the "19. SmartNormalize" algorithm to any model to improve it in the way described below (see "What will it give?")
...
You have a stone that you consider beautiful in the terms of balance between mass and optical parameters - you want similar diamonds to be the result of your cutting process. Scan it and then apply Smart Normalize to remove any imperfections of the built model, then register the result as your in-house cut. Stick future solutions to this cut with the hybrid appraiser and enjoy beautiful and massy diamonds of your desired shape.
...
| Note |
|---|
For creating in-house cuts and as allocation forms only the scanned models or solutions with a good balance of mass and optical properties should be used. See Cut evolution. |
Scenario 3 - normalize model to use it as a sample during scanning
...
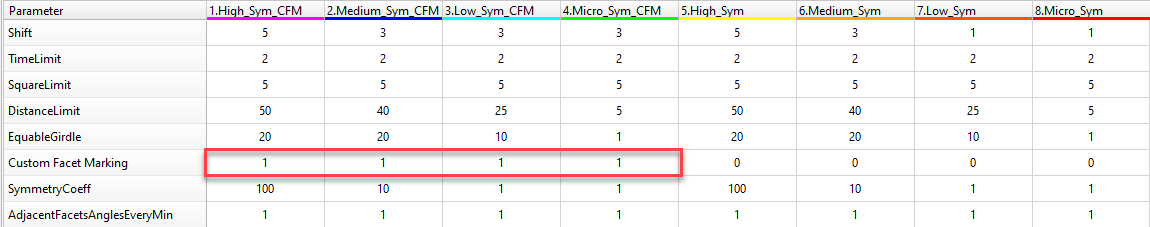
- Shift - the distance that vertices can move away from the starting position during rebuilding. Necessary for the case when the Adjacent Facets Angle between facets is small and a slight change of the facet normals may result in a large vertex translation. The small Shift may block solution search when Custom Facet Marking is enabled.
- TimeLimit - a maximum running time of one rebuild. Stops the preset processing if the algorithm cannot rebuild the model.
- SquareLimit - small facets deletion threshold. Facet areas of the model proportionally transformed to 1ct weight are compared with this threshold. "5" = 5000 µm^2.
- DistanceLimit - short edges deletion threshold, Edge lengths of the model proportionally transformed to 1ct weight are compared with this threshold. Value is in µm. The threshold is divided into absolute and relative parts. The relative part reduces depending on the size of the horizontal section of the model on the height of the specific edge. Therefore, at the culet level where the section is minimal, smaller edges can be kept than at the level of a girdle where the section is maximal.
- EquableGirdle - quadrangular girdle facets that belong to one sector, that is they touch the same crown and pavilion Half facets, should have approximately the same length. The less this parameter is, the less deviation in edge length is acceptable in one sector during a rebuild.
Custom Facet Marking - if enabled (any value different from "0", usually "1") for the preset then this preset takes into consideration the facet types: the facets from the same group will obtain the same Slope Angle.
On the picture:
- "Sym" presets work only with the symmetry axis
- "Sym"+"CFM" presets work with the symmetry axis and custom facet marking (CFM)
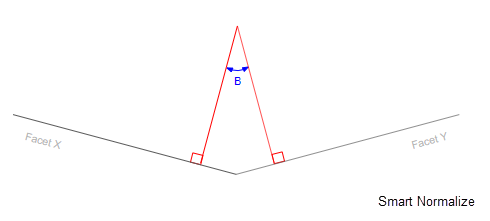
SymmetryCoeff - The Deviation from start and Symmetry metrics contradict. This parameter sets how many times the increase in symmetry is more important than minimizing the normals deviation.
Note title Note In all current presets the SymmetryCoeff differs from "0" to prevent users from selecting the asymmetrical models when this should not be done. The algorithm was configured for the models having from 1 to 9 symmetry axes. If all the presets produce distorted models, one of the probable reasons is the errors in the detection of symmetry axes or the pairs of symmetrical facets. This may be caused by the large asymmetry of the initial model or the non-standard number of symmetry axes. In this case try specifying facet types, then set SymmetryCoeff to "0" and run Smart Normalize without Symmetry.
- AdjacentFacetsAnglesEveryMin - sets limitation “not less than this value” for the angle between normals of any neighboring facets (see details in Adjacent Facets Angles).
Recommendations on usage
...
- To improve output, specify facet types for the initial model. This:
- will guarantee deleting of excess facets
- is necessary for working with enabled Custom Facet Marking parameter (see above)
- the facet types are automatically transferred to the resulting model which is useful during registering it as a new in-house cut
On Stage 1 (see above) the symmetrical sectors of the model which will in Stage 3 become of the same length, may have large differences in length. Because of this, the different number of girdle facets can go to non-symmetrical sectors. This can lead to poor performance of the Smart Recut algorithm for such models. If this situation occurs, it is recommended to run the Smart Normalize algorithm one more time - it should divide a girdle into facets correctly because initially, the sectors have the same length.
Before SN After 1st run of SN After 2nd run of SN a
- The small value of the Shift parameter may block solution search when Custom Facet Marking is enabled.
If all the presets produce distorted models, one of the probable reasons is the errors in the detection of symmetry axes or the pairs of symmetrical facets. This may be caused by the large asymmetry of the initial model or the non-standard number of symmetry axes. In this case try specifying facet types, then set SymmetryCoeff to "0" and run Smart Normalize without Symmetry.
For square cuts, the algorithm enforces the final GidleRatio to 1.0 to reach the corresponding symmetry.
The algorithm can work with the models in which crown and pavilion touch in a vertex or edge. For such cases, the facet types must be specified.
- Nonconvex heart cuts are supported by Smart Normalize and Smart Recut. However, in the case of Hearts, the algorithm more often has difficulties with the girdle shape and finding the correct symmetry axes for the scanned models. Thus for building Heart allocation forms it is better to use the models created in the Cut Designer or the solutions of Recut or Smart Recut algorithms.
...
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|