Overview
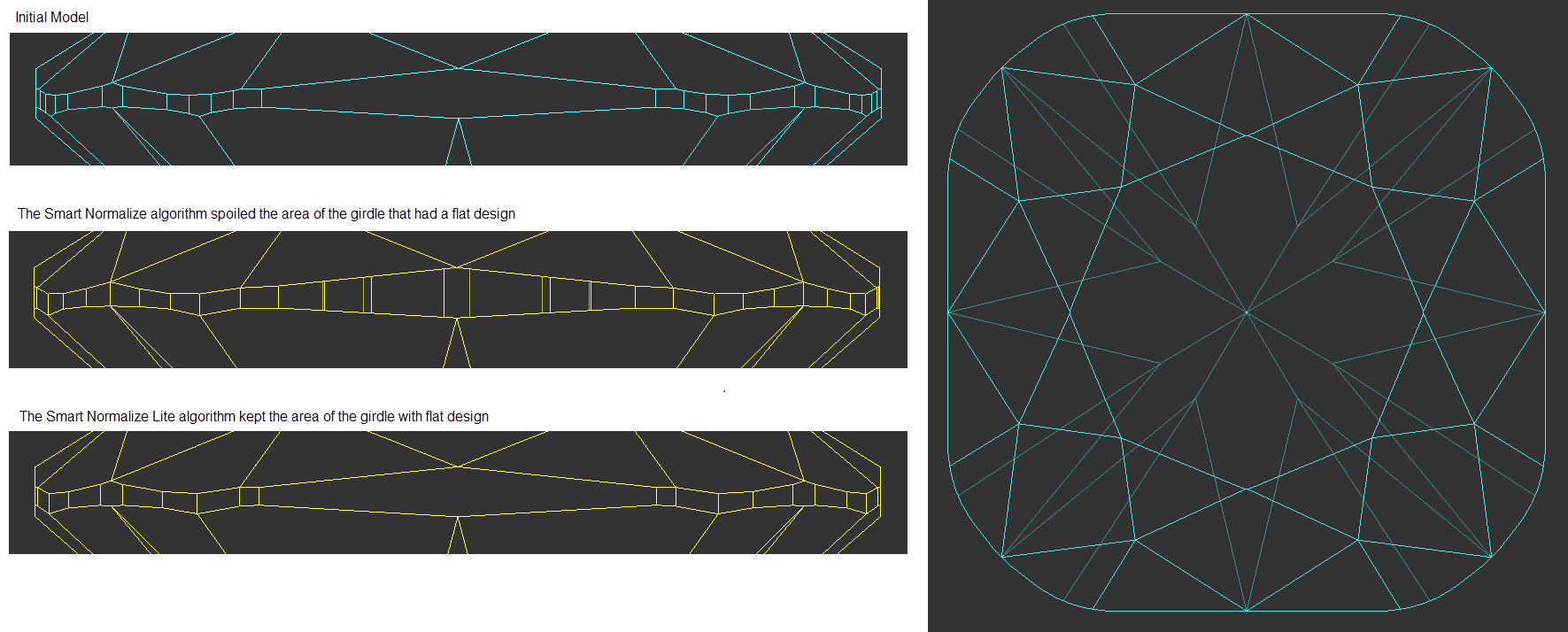
The "19. SmartNormalizeLite" algorithm may be used algorithm is intended for the normalization of brilliants with the specific girdle design - in contradiction to usual SmarNormalize of cuts without a girdle. The algorithm does not consider a girdle to be a specific set of facets the particular properties. In contradiction to the usual SmarNormalize, this algorithm does not attempt to make a girdle strictly vertical. Thus, the algorithm may be used for normalizing the designer cuts for later optimizing without changing the form (using the "19. Single (FixedForm)" algorithm of the In-house cut workflow).The SmartNormalizeLite algorithm should be used only for cuttings. The algorithm does not attempt to break the girdle into equal facets. The algorithm can delete the initial girdle if its height is small, which can cause non-obvious problems during the further usage of such a cut.
| Note |
|---|
Do not use the "19. SmartNormalizeLite" algorithm for the cuts with girdle it the 19. Smart Normalize algorithm provides the appropriate result. |
| Smart Normalize | Smart Normalize Lite - Girdle Kept | Smart Normalize Lite - Girdle Deleted |
|---|
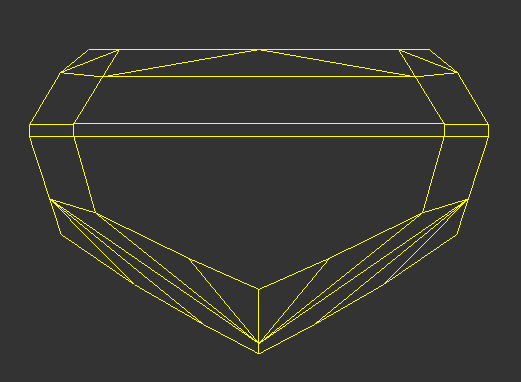 Image Added Image Added
| 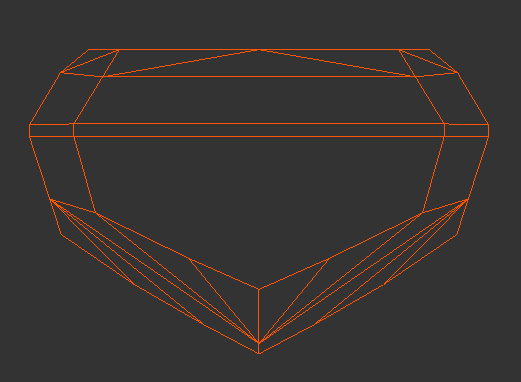 Image Added Image Added
| 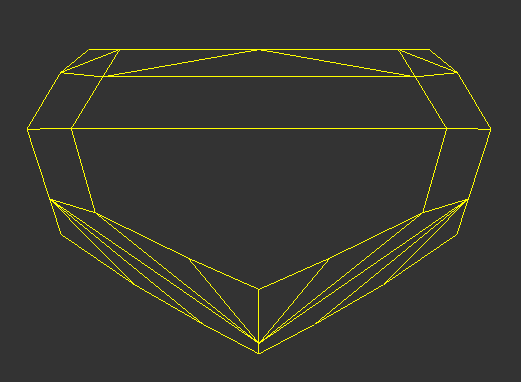 Image Added Image Added
|
In non-standard situations, the "19. SmartNormalize" algorithm may produce unexpected results towards a girdle of a cut. If you estimate the girdle of the initial model as better than the created solution has, you can try running the "19. SmartNormalizeLite" algorithm for the cuts:
- created in Cut Designer or other software for producing ASCII cuttings
- not-rounded scans without significant flaws
| Note |
|---|
Such cuts are recommended to be used only for later optimizing without changing the form (using the "19. Single (FixedForm)" algorithm of the AnyCut Workflow). |
| Note |
|---|
Cuttings Cuts created with the SmartNormalizeLite are not guaranteed to work correctly with the SmartRecut AnyCut. |
Related pages



